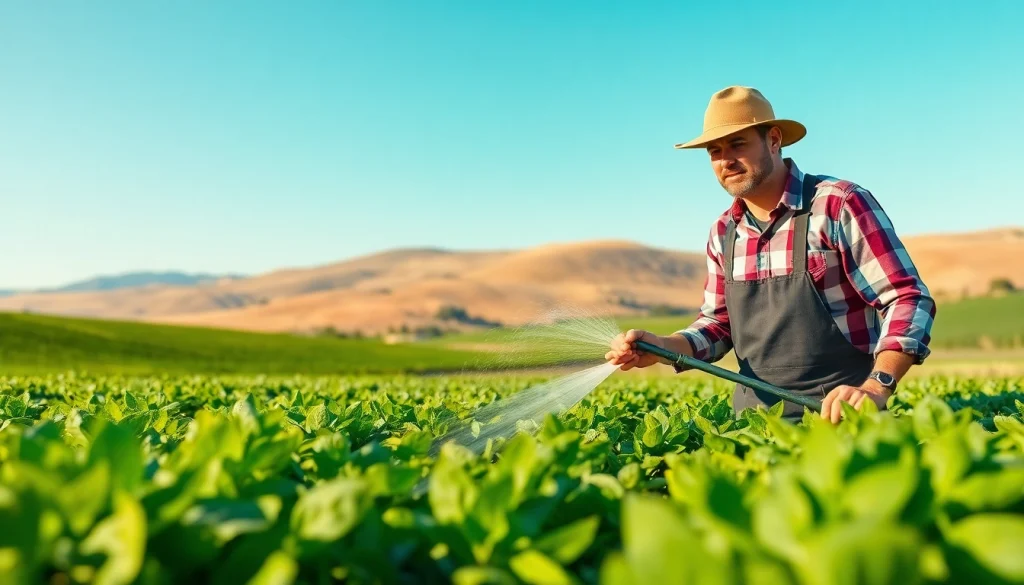
Understanding Land Irrigation: Basics and Benefits
Land irrigation is a critical practice in modern agriculture, serving as a lifeline for crop production, especially in areas with irregular rainfall patterns. As the world faces increasing food demands and climate variability, understanding land irrigation becomes essential for sustainable agricultural practices. This article delves into the principles, importance, challenges, and advancements in land irrigation, providing a comprehensive overview tailored for agricultural professionals and enthusiasts alike.
What is Land Irrigation?
Land irrigation involves the application of controlled amounts of water to crops at regular intervals to assist their growth. This method transforms regions that would otherwise be arid or semi-arid into productive agricultural land, serving as the backbone for food production in many countries. By ensuring that crops receive adequate moisture, farmers can optimize yield and quality. The underlying principles of land irrigation are steeped in both ancient practices and modern technological innovations, making it a diverse field worth exploring.
Importance of Land Irrigation for Agriculture
The relevance of land irrigation in agriculture cannot be overstated. Here are key points highlighting its importance:
- Enhanced Crop Yield: Consistent watering improves crop performance and mitigates risks associated with drought, leading to stable and higher yields.
- Soil Health: Proper irrigation prevents soil erosion, maintains soil fertility, and controls salinity, ultimately enhancing soil structure and health.
- Water Management: Effective irrigation practices contribute to better water use efficiency, reducing waste and ensuring that every drop counts.
- Sustainability: Irrigation allows for diversified cropping systems and year-round farming, which enhances food security and promotes sustainability in agriculture.
Types of Land Irrigation Systems
There are several types of land irrigation systems employed globally, each with distinct advantages and applications:
- Surface Irrigation: Water flows over the soil surface, being absorbed by the crops. It’s one of the oldest methods and is often cost-effective but requires careful management to avoid water pooling and erosion.
- Drip Irrigation: This low-pressure system delivers water directly to the plant roots through a network of pipes and emitters, significantly reducing water waste and promoting efficient growth.
- Sprinkler Irrigation: Water is simulating rainfall through a system of pipes, valves, and spray heads. It’s flexible and can be used on various terrains but requires a good energy source for operation.
- Subsurface Irrigation: This technique involves burying drip lines below the soil surface, providing water directly to the plant roots while minimizing evaporation losses.
Common Challenges in Land Irrigation
Despite its advantages, land irrigation faces several challenges that can undermine its effectiveness:
Poor Water Management
One of the primary challenges is inefficient water management. Misallocation of water resources can lead to over-irrigation, which raises costs and encourages water wastage while undermining soil health. Effective management practices, including proper scheduling and monitoring, are essential to mitigate these issues.
Soil Salinity Issues
Salinity is a major concern in irrigated landscapes where excessive water can lead to salt accumulation in the soil. Saline soils can severely hinder plant growth, making it vital for farmers to monitor and manage salinity levels through practices like leaching and crop rotation.
Climate Impact on Irrigation Needs
Climate change introduces variability in rainfall patterns, affecting water availability for irrigation. Farmers must adapt their irrigation methods in response. Utilizing historical data and predictive models is crucial in planning irrigation schedules to match changing weather patterns.
Advanced Techniques for Effective Land Irrigation
Adopting advanced irrigation techniques can optimize efficiency and ensure sustainable agricultural practices:
Drip Irrigation: Precision at Its Best
Drip irrigation represents a significant leap forward in irrigation technology. By delivering precise amounts of water directly to the plant roots, farmers can enhance water uptake and minimize evaporation. Drip systems are particularly beneficial in regions with water scarcity, making them indispensable for sustainable farming practices.
Benefits of Sprinkler Systems
Sprinkler systems are versatile and capable of covering large areas quickly. They can be tailored to address specific crops’ needs through adjustable rates of flow and timing. This adaptability makes them suitable for various farming operations, ensuring comprehensive coverage and reduced labor costs.
Using Smart Technology for Better Efficiency
The incorporation of smart technologies, such as soil moisture sensors, automated irrigation systems, and data analytics, has revolutionized land irrigation practices. These tools allow farmers to monitor soil conditions in real time, improving water management and promoting efficient use of resources.
Cost-Effective Land Irrigation Solutions
Implementing cost-effective solutions for land irrigation is vital for enhancing sustainability and profitability:
Investing in Sustainable Materials
Choosing sustainable materials for irrigation systems can lead to reduced long-term costs and environmental impact. Utilizing recyclable materials and energy-efficient pumps not only lowers operational costs but also aligns with sustainable agriculture principles.
Government Assistance and Resources
Many governments offer assistance programs for farmers seeking to implement or upgrade irrigation systems. These resources can include financial support, grants, and technical assistance aimed at enhancing water efficiency and promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
Long-Term Savings through Efficient Practices
While initial investments in modern irrigation systems may be substantial, the long-term savings achieved through efficient water use, reduced labor costs, and increased yields can make these practices financially beneficial over time. Farmers should consider these factors when planning their irrigation strategies.
Measuring the Success of Land Irrigation Practices
Evaluating the effectiveness of land irrigation practices is critical for continuous improvement:
Key Performance Indicators for Irrigation
Identifying key performance indicators (KPIs) such as water use efficiency, crop yield/acre, and irrigation cost/acre is essential. Regular monitoring of these indicators helps farmers understand the impact of their irrigation practices, guiding them in making informed decisions.
Reviewing Crop Yield Data
Analyzing crop yield data over time allows farmers to assess the effectiveness of their irrigation strategies. Variations in yield can provide insights into necessary adjustments in irrigation methods, fostering a cycle of continuous improvement.
Adapting Strategies Based on Performance Metrics
Farmers should remain flexible, adapting their irrigation strategies based on performance metrics and changing conditions. Regular reviews of water management practices will facilitate enhanced crop performance and sustainability.
FAQs:
1. What is land irrigation? Land irrigation is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to crops to promote their growth and optimize yields.
2. What are the benefits of land irrigation? Benefits include increased crop yields, improved water conservation, and the ability to cultivate crops in arid climates.
3. How can I choose the right irrigation system? Assess your crop needs, local conditions, and soil characteristics, then consult with agricultural experts for tailored recommendations.
4. What difficulties can arise with land irrigation? Potential difficulties include water shortages, soil salinity, and inadequate system management, impacting crop health.
5. How can technology improve land irrigation? Smart technologies enhance efficiency through better water management, optimizing irrigation levels, and reducing waste.